When An Rna Strand Forms Using Dna As A Template
When An Rna Strand Forms Using Dna As A Template – Ruairi is a senior research writer at Technology Networks. He holds an MSc in Clinical Neuroscience from the University of Cambridge and has been writing for Technology Networks since 2018.
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are perhaps the most important molecules in cell biology, responsible for storing and reading the genetic information that underlies all life. They are both linear polymers made up of sugars, phosphates and bases, but there are some key differences that set them apart
When An Rna Strand Forms Using Dna As A Template

. These differences allow the two molecules to work together and fulfill their important roles. Here we look at 5 key differences between DNA and RNA. Before we delve into the differences, let’s look at these two nucleic acids side by side.
Stages Of Transcription: Initiation, Elongation & Termination (article)
There are several differences that separate DNA from RNA. These include the functions of the two molecules, their structure, their average length, the sugars (DNA contains deoxyribose and RNA contains ribose) and base molecules (RNA contains uracil instead of thymine) they contain, their positions, and their reactivity to enzymes and UV. light.

DNA copies and stores genetic information. This is a diagram of all the genetic information contained in the body.
RNA converts the genetic information contained in DNA into a form used to make proteins and then carries it to the ribosomal protein factories.
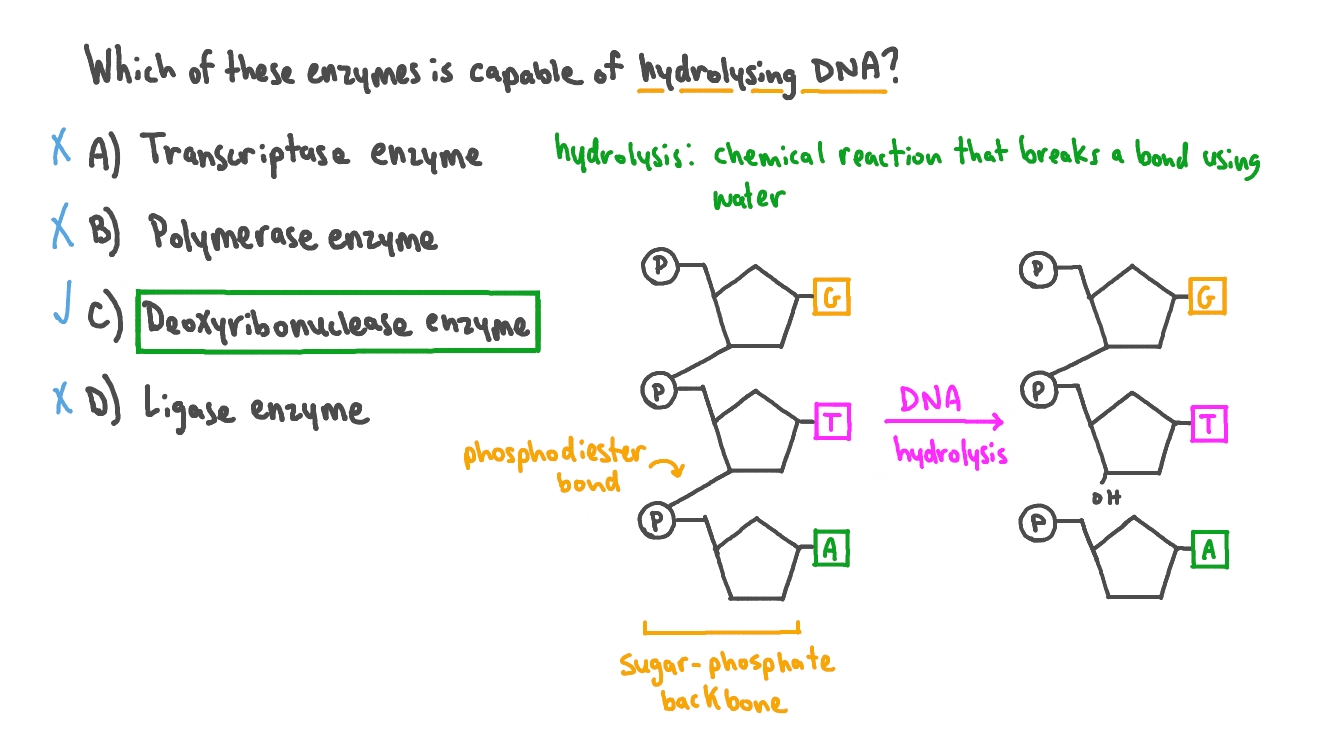
The Chemical Structure Of Dna
DNA consists of two strands arranged in the form of a double helix. These strands are made up of subunits called nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a phosphate, a 5-carbon sugar molecule, and a nitrogenous base.
RNA has only one strand, but like DNA, it is made up of nucleotides. RNA strands are shorter than DNA strands. RNA sometimes forms a double helix secondary structure, but only intermittently.
DNA is a much longer polymer than RNA. Chromosome, for example, is a single long DNA molecule, the length of which in the untwisted form will be several centimeters.
Lecture 4 By Ms. Shumaila Azam
RNA molecules are variable in length, but are much shorter than the long DNA polymers. A large RNA molecule can be only a few thousand base pairs long.

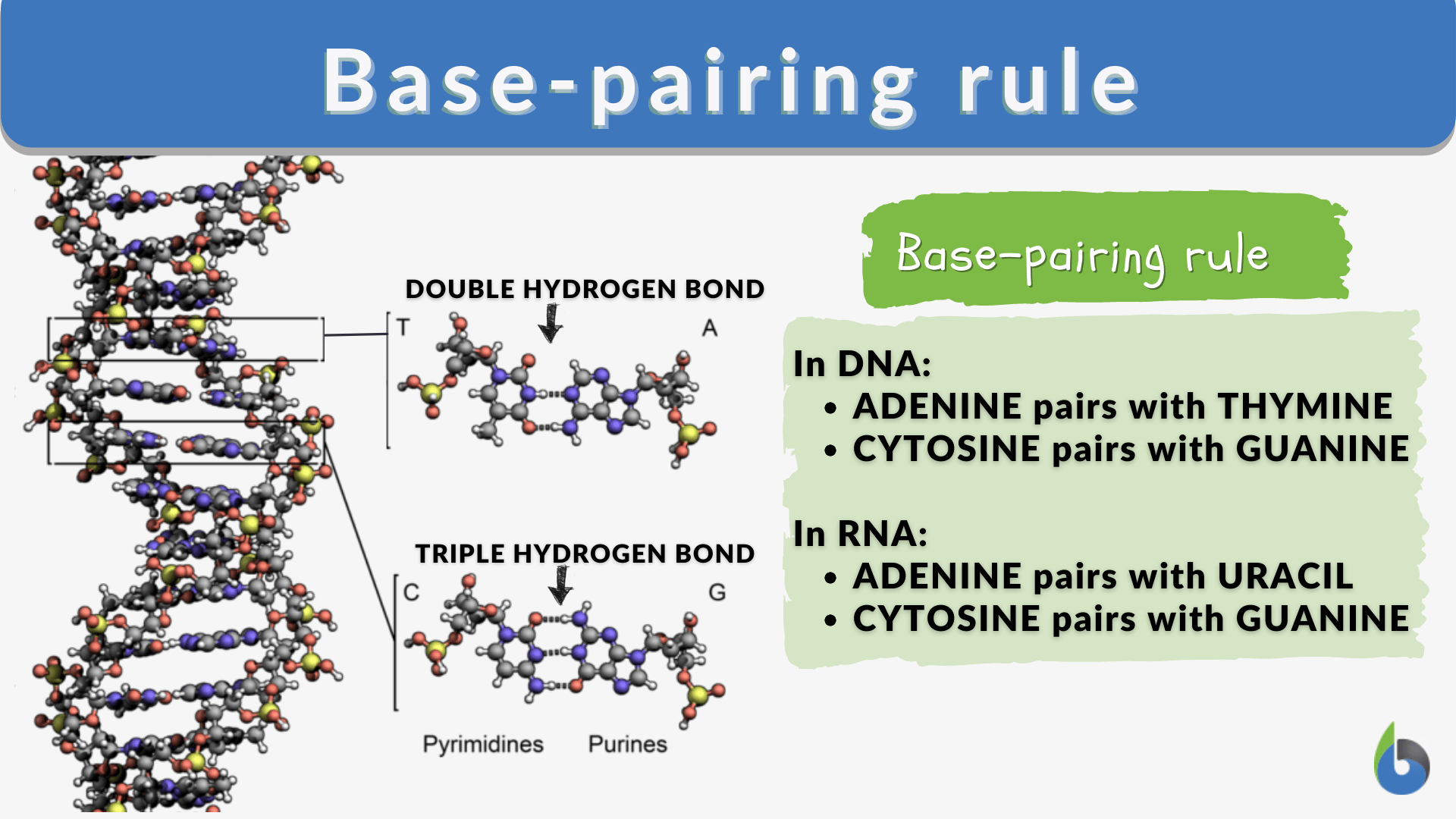
RNA shares adenine (“A”), guanine (“G”), and cytosine (“C”) from DNA, but contains uracil (“U”) instead of thymine.
RNA is made in the nucleus and then moves to specialized areas of the cytoplasm depending on the type of RNA formed.

Translation Vs. Transcription: Similarities And Differences
Because of the deoxyribose sugar, which contains one less oxygen-containing hydroxyl group, DNA is a more stable molecule than RNA, which is useful for a molecule tasked with keeping genetic information safe.
RNA, which contains the sugar ribose, is more reactive than DNA and unstable under alkaline conditions. The larger helical grooves of RNA mean that enzymes attack it more easily.

DNA encodes all genetic information and is the blueprint from which all biological life is created. And this is only in the short term. In the long run, DNA is a data storage device, a biological flash drive that allows the blueprint of life to be passed down between generations
Transcription Translation And Replication Notes: Diagrams & Illustrations
. The RNA acts as a reader that decodes this flash drive. This reading process is multi-step, and there are specialized RNAs for each of these steps. Below we take a closer look at the three most important types of RNA.

Both DNA and RNA are built from a sugar base, but while the sugar in DNA is called deoxyribose (pictured left), the sugar in RNA is simply called ribose (pictured right). The prefix “deoxy” indicates that while RNA has two hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached to its carbon base, DNA has only one, with a single hydrogen atom attached instead. The extra hydroxyl group in RNA proves useful in the process of converting the genetic code into mRNA, which can be turned into proteins, while the deoxyribose sugar gives DNA more stability
The nitrogenous bases in DNA are the basic units of the genetic code, and their correct order and combination are essential for biological function. The four bases that make up this code are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). The bases are paired with each other in a double helix structure, these are pairs of A and T, as well as C and G. RNA does not contain thymine bases, replacing them with uracil (U) bases that connect to adenine

Life’s First Peptides May Have Grown On Rna
While the ubiquity of the double helix of DNA by Francis Crick and James Watson (or should that be Rosalind Franklin?) means that the double-stranded structure of DNA is common knowledge, the single-stranded form of RNA is not so well known. RNA can form into double-stranded structures, such as during translation, when mRNA and tRNA molecules pair up. DNA polymers are also much longer than RNA polymers. the 2.3-meter-long human genome consists of 46 chromosomes, each of which is one long DNA molecule. In comparison, RNA molecules are much smaller
Eukaryotic cells, including all animal and plant cells, store most of their DNA in the nucleus, where it exists in a tightly packed form called a chromosome
. This compact form means that DNA can be easily stored and transported. In addition to nuclear DNA, some DNA exists in the energy-producing mitochondria, small free-floating organelles in the cytoplasm, the region of the cell outside the nucleus.
Nucleic Acid Structure
The three types of RNA are found in different locations. mRNA is made in the nucleus, with each mRNA fragment being copied from its associated DNA fragment before leaving the nucleus and entering the cytoplasm. The fragments are then moved around the cell as needed using the cell’s internal transport system, the cytoskeleton. tRNA, like mRNA, is a free-floating molecule that moves around the cytoplasm. When it receives the correct signal from the ribosome, it will search for amino acid subunits in the cytoplasm and deliver them to ribosomes for incorporation into proteins.

. rRNA, as mentioned earlier, is found in ribosomes. Ribosomes are formed in a region of the nucleus called the nucleolus before being exported to the cytoplasm, where some ribosomes float freely. Other cytoplasmic ribosomes are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum, a membrane structure that helps process proteins and transport them out of the cell
The structure we’ve described in this article is certainly the most common form of DNA, but it’s not the whole story. There are other forms of DNA and RNA that destroy the classic structures of these nucleic acids.

Intro To Rna Biology: Cartoon Edition
Z-DNA While the DNA structure you’ll see above—and in any biology textbook you might open—has a right-handed helix, there are also left-handed DNA molecules. These are known as Z-DNA. Normal, “classic” DNA is called B-DNA.
Z-DNA is thought to play a role in the regulation of gene expression and may be formed by DNA-processing enzymes such as DNA polymerase.

A-DNA Recognized by Rosalind Franklin at the same time as B-DNA, A-DNA is an alternative DNA structure that often occurs when the molecule is dehydrated. Many crystal structures of DNA are in the A-DNA form. It has a smaller structure with a different number of base pairs per turn and tilt than B-DNA. The biological significance of A-DNA has expanded greatly in recent years, and it is now recognized that A-DNA is involved in many roles, including:
Rna / Dna
Triple Helix DNA The triple helix structure of DNA can be formed when certain nucleic bases—pyrimidine or purine—occupy the major grooves of normal B-DNA. This can occur naturally or as part of a deliberate strategy to modify DNA for research purposes.
Triplex-forming oligonucleotides (TFOs) can bind conventional double-stranded DNA, which can help target agents used for DNA modification to specific genomic locations. H-DNA is an endogenous triple-stranded DNA molecule that promotes genome mutation.
DsRNA Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) is most often the genomic backbone of many plant, animal, and human viruses. These include Reoviridae and rotaviruses, which cause diseases such as gastroenteritis. dsRNA molecules are powerful immunogens – they activate the immune system, which then cuts the dsDNA as a defense mechanism. The discovery of the protein mechanism that enables this reaction led to the development of RNAi gene silencing technology, which won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2006. Today’s post moves into the realm of biochemistry with a look at the chemical structure of DNA and the role of protein production in our cells. Of course, DNA is not only found in humans – it is present in the cells of every multicellular life form on Earth. This figure gives an overview of its general structure in these life forms and a brief explanation of how it allows proteins to be produced.

Chapter 10: Transcription And Rna Processing
DNA is contained in the nucleus of cells of multicellular organisms and was first isolated in 1869 by the Swiss doctor Friedrich Miescher. However, its structure was not elucidated until nearly a century later, in 1953. The authors of the paper that proposed this structure, James Watson and Francis Crick, are now household names and won the Nobel Prize for their work. This work, however, relied heavily on the work of another scholar, Rosalind Franklin.
Franklin herself also studied the structure of DNA, and it was her X-ray image, which clearly shows the structure of the double helix of DNA, that greatly helped their work. She had not yet published her findings when Watson and Crick accessed them, without

Dna strand to rna strand, using whole life insurance as an investment, rna strand from dna, rna template strand, using baking soda as an antacid, using sharepoint as an intranet, dna and rna template, dna rna strand, dna strand to rna converter, dna template to rna, when an rna strand forms using dna as a template, dna and rna strand
Thank you for visiting When An Rna Strand Forms Using Dna As A Template. There are a lot of beautiful templates out there, but it can be easy to feel like a lot of the best cost a ridiculous amount of money, require special design. And if at this time you are looking for information and ideas regarding the When An Rna Strand Forms Using Dna As A Template then, you are in the perfect place. Get this When An Rna Strand Forms Using Dna As A Template for free here. We hope this post When An Rna Strand Forms Using Dna As A Template inspired you and help you what you are looking for.
When An Rna Strand Forms Using Dna As A Template was posted in January 4, 2023 at 5:28 am. If you wanna have it as yours, please click the Pictures and you will go to click right mouse then Save Image As and Click Save and download the When An Rna Strand Forms Using Dna As A Template Picture.. Don’t forget to share this picture with others via Facebook, Twitter, Pinterest or other social medias! we do hope you'll get inspired by SampleTemplates123... Thanks again! If you have any DMCA issues on this post, please contact us!


